
Blackheads (Open Comedones)
These are small, dark spots caused by a clog of oil and dead skin cells in the hair follicle. The black appearance is due to oxidation, not dirt.
Acne is a common skin condition affecting many people worldwide, but its forms and causes can vary significantly. Understanding the different types of acne is essential for identifying the most effective treatment methods and achieving clear, healthy skin. This comprehensive guide explores the various forms of acne, their causes, symptoms, and best treatment options.
Think of acne like your skin’s way of acting out. It happens when hair follicles get clogged up with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. That’s what causes those pesky pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Sometimes, acne can even lead to more serious stuff like cysts and nodules. It’s most common on areas like your face, chest, back, and shoulders because these areas have more oil-producing glands.
Imagine your skin as a garden. Each pore is like a tiny hole in the ground, and when everything’s flowing smoothly, oil and dead skin cells pass through just fine. But when too much oil and dead cells clog a pore, it’s like blocking a hole in your garden. The clog causes bacteria to get trapped, leading to a pimple. Keeping your “garden” (aka your skin) clean is super important for avoiding those breakouts.
Let’s talk about why acne happens. There are a few big reasons:
Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, pregnancy, or even your period, can kick your oil glands into overdrive, clogging pores and leading to acne. Hormones like androgens (testosterone, for example) play a major role in this process.
Yep, you can thank your family for this one. If your parents had acne, chances are you might deal with it too. Genetics can determine how active your oil glands are and how your body responds to bacteria.
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, lithium, and some birth control pills, can trigger or worsen acne. These medications can alter hormone levels or cause skin cells to increase rapidly, contributing to clogged pores.
There’s still research being done on how diet affects acne, but some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods, dairy, and sugary snacks could make acne worse by increasing insulin and oil production.
While stress doesn’t directly cause acne, it definitely makes it worse. Stress can increase inflammation and oil production, often showing up as breakouts along the jawline and chin.
Acne is categorised into two main types: non-inflammatory and inflammatory. Each type has its own characteristics and causes. Acne is not a one-size-fits-all condition. Different types of acne have distinct characteristics and require specific treatments. Here are the most common types:
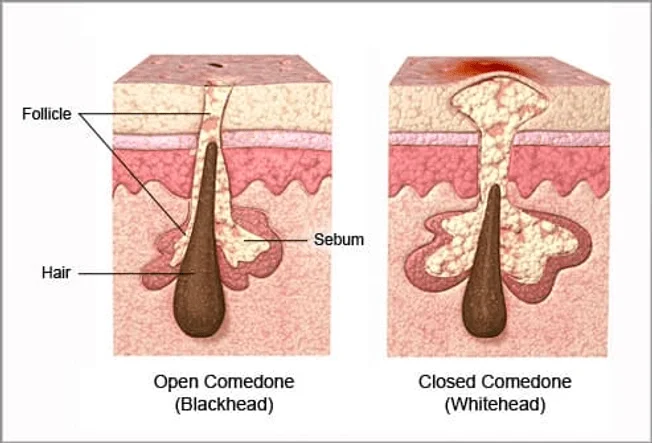
Comedonal acne is characterised by non-inflammatory lesions and is primarily caused by clogged hair follicles. A comedo is a blocked hair follicle caused by oil and dead skin cells. When this happens, it can turn into a bump, like a whitehead or blackhead. Products that clog pores and cause these bumps are called “comedogenic.” On the other hand, makeup labelled “noncomedogenic” is less likely to block pores and cause acne.
You’re in luck! Many brands in India, like Neutrogena, La Roche-Posay, and Clinique, offer non comedogenic makeup. You can find these on popular sites like Amazon, Nykaa, and Myntra.
Many makeup products in India are labelled as “non-comedogenic,” meaning they are less likely to clog pores and cause acne. Some examples of non-comedogenic makeup brands available in India include:
These products are on major online platforms like Amazon India, Nykaa, and Myntra.
Look for "non-comedogenic" on the product labels or descriptions when shopping.
Look for “non-comedogenic” on the product labels or descriptions when shopping.
This type of comedonal acne includes:
These are small, dark spots caused by a clog of oil and dead skin cells in the hair follicle. The black appearance is due to oxidation, not dirt.

These are small, flesh-coloured or white bumps caused by clogged hair follicles that are closed at the skin’s surface.
For more insights, read our post on Whiteheads: Effective Ways to Manage and Treat.
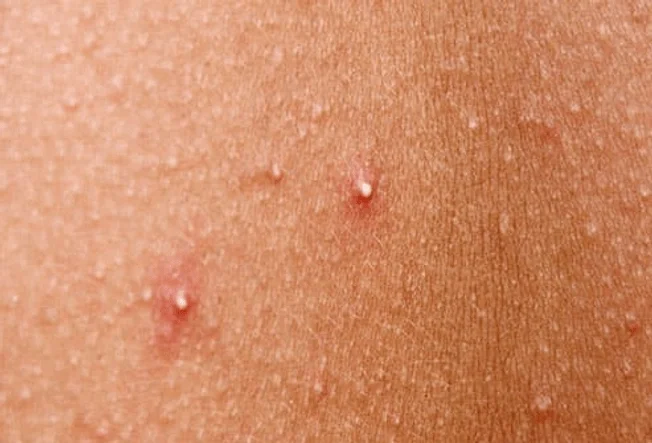
Inflammatory acne occurs when bacteria infect clogged pores, leading to inflammation. This type of acne is often more severe and can be painful. It includes:
These are small, red bumps without pus. Inflammation causes these around the hair follicles.
Need skincare tips? Our blog on How to Treat Papules has you covered.
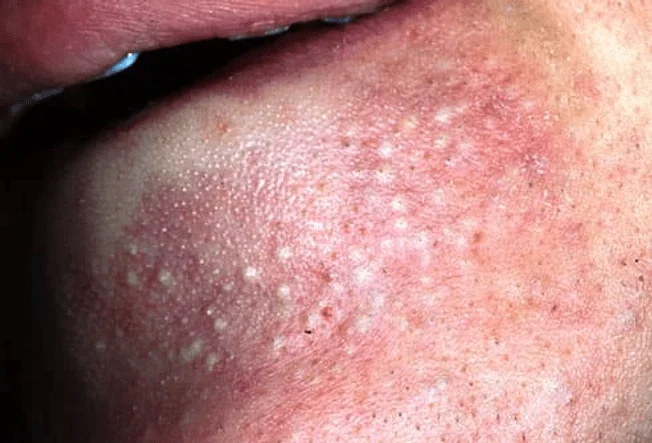
Similar to papules but with a white or yellow center filled with pus.
Learn how to deal with them in Understanding Pustules: What They Are and How to Get Rid of Them.
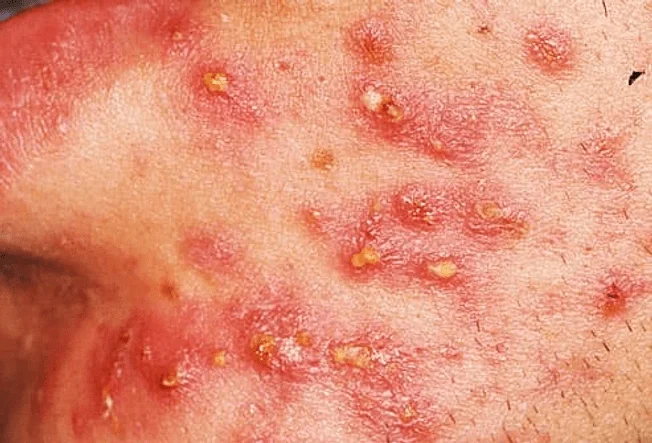
These painful, deep bumps are more severe than papules and pustules, and they can lead to scarring.
Find out how to handle these stubborn bumps in Dealing with Nodules.
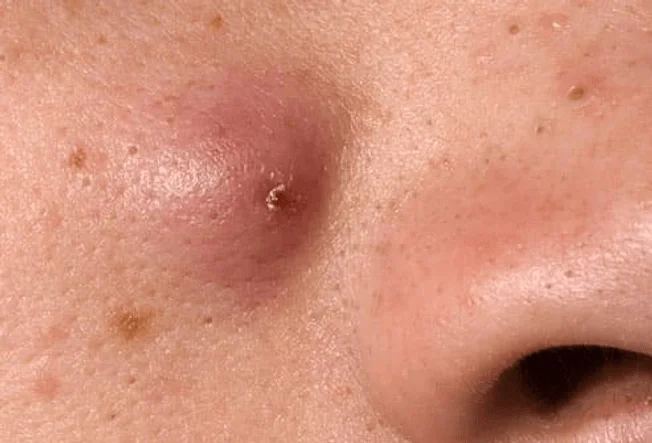
These are the most severe form of acne- deep, painful lumps beneath the skin that often need medical treatment.
For more on cystic acne, check out our blog on Cystic Acne: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Tips.
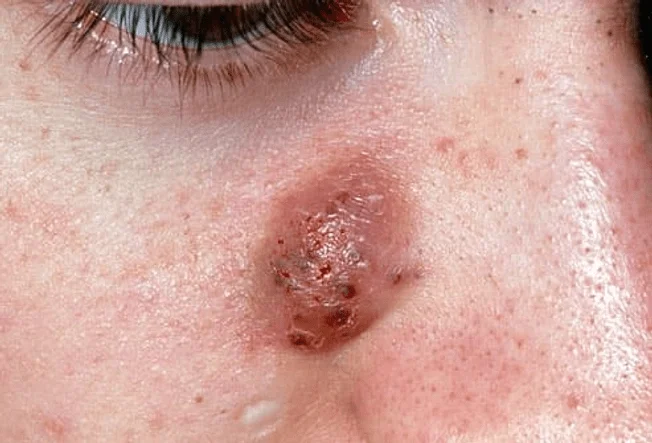
Acne mechanica is caused by friction, pressure, heat, and constant skin rubbing. It is commonly seen in athletes, military personnel, and individuals who wear tight clothing or headgear.
Hormonal acne is often seen in women and is usually triggered by hormonal changes related to menstruation, pregnancy, menopause, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This type of acne typically appears around the jawline and chin.
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast within hair follicles, leading to itchy, uniform pimples often mistaken for bacterial acne. This condition is often exacerbated by humidity, sweat, and excessive use of skin products.
To know whether any specific skin product is causing you fungal acne, you can enter details in the ‘fungal acne ingredient checker.’
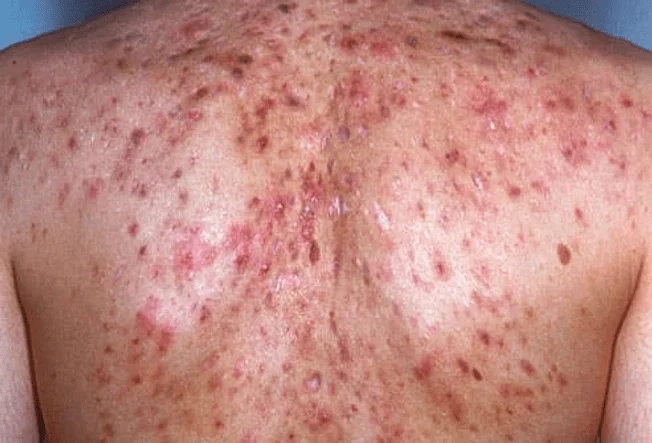
Severe acne includes conditions like:
Knowing your type of acne can make all the difference when it comes to treatment. Here’s a quick guide to help you figure it out:
Feature | Benzoyl Peroxide | Salicylic Acid | Retinoids |
Primary Action | It kills bacteria and reduces oil production | Exfoliates dead skin cells and unclogs pores | Promotes cell turnover and prevents clogged pores |
How It Works | Releases oxygen to kill acne-causing bacteria | Dissolves the type of skin debris that clogs pores | Increases the rate of skin cell replacement |
Best For | Inflammatory acne, such as pustules and cysts | Comedonal acne like blackheads and whiteheads | Both comedonal and inflammatory acne, anti-aging |
Common Formulations | Creams, gels, and washes | Cleansers, toners, creams, and serums | Creams, gels, and serums |
Side Effects | Skin irritation, dryness, redness, and bleaching | Mild irritation and dryness | Dryness, redness, increased sensitivity to sunlight |
Usage Tips | Start with lower concentrations to minimise irritation | Use consistently as part of a daily skincare routine | Use at night due to increased sensitivity to sunlight |
Precautions | Avoid using near eyes, mouth, and sensitive areas | Avoid using with other strong acids or retinoids | Do not use it if pregnant without consulting a doctor |
Did You Know? 🌿🔍
While natural remedies like tea tree oil and aloe vera offer gentler alternatives to harsh chemicals, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Studies show that integrating these with a healthy diet and stress management can enhance their effectiveness.
However, it’s crucial to patch-test any natural product before full application, as natural doesn’t always mean irritation-free!
Each of these treatments offers a unique approach to tackling tough acne problems, providing solutions that are as rapid as they are effective.
Effective acne prevention involves a combination of skincare routines, diet, and lifestyle changes:
While mild acne can often be managed with over-the-counter products and lifestyle changes, severe or persistent acne should be evaluated by a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide prescription medications, professional treatments, and guidance that suits your skin.
Acne is a complex condition with various types, causes, and treatment options. Understanding the types of acne is the first step towards effective management and achieving clear, healthy skin.
If you are struggling with acne, remember that you are not alone and that help is available. Explore related articles on our site to learn more about specific types of acne and the most effective treatments. Together, we can help you achieve the clear skin you deserve.
By understanding the different types of acne and their specific characteristics, you can take the first step toward effective management and clearer skin.
While acne can be managed and treated effectively, it may not be completely curable for everyone. It often depends on the underlying cause and severity.
Popping pimples leads to scarring and further infection. To avoid this, it’s best to let the pimple heal naturally or seek professional treatment.
Nodules are hard, painful bumps that form deep in the skin, while cysts are softer, pus-filled, and often larger than nodules.
Most acne treatments take at least 4-6 weeks to show significant results. Consistency is key to seeing improvement.
Surprisingly- Yes!, diet can play a role in acne development. High sugar and dairy intake have been linked to increased acne breakouts.
Acne scars are marks that can be seen on the skin after acne has healed. They can range from slight discolouration to deep indentations. The severity and type of scarring often depend on the acne and how it is treated.
Acne scars are caused by the skin’s healing process after severe acne, such as cysts or nodules, damages the deeper layers of the skin. When the body tries, collagen, a protein that helps the skin heal, is produced. If too little or too much collagen is produced, it can result in different types of acne scars, such as raised (hypertrophic) or indented (atrophic) scars.
Acne scars are grouped into several types:
Yes, early and effective treatment of acne can reduce the risk of scarring. Don’t pick or squeeze pimples, as this can increase the likelihood of scarring. Using proper acne treatments and consulting a dermatologist for severe cases can help minimise scarring.
Treatment options for acne scars include:
Natural remedies which include the use of aloe vera, honey, and vitamin C, help improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. However, they are generally less effective on deeper scars and may not provide the same results as professional treatments.
The healing time for acne scars varies depending on the type of scar and the treatment used. Mild scars may fade over a few months with proper care, while more severe scars might require several treatment sessions over months or even years.
If you have persistent or severe scarring that is affecting your confidence or skin health, it’s a good idea to consult a dermatologist. They can recommend professional treatments depending on your skin type.